What Can Destroy Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is a tough and versatile material that is used in a wide variety of applications. It is known for its strength and resistance to corrosion, but there are certain conditions and substances that can cause it to corrode or degrade. Depending on the grade, stainless steel can be vulnerable to various forms of attack, such as pitting, staining, and even cracking. In some cases, these issues can be caused by improper maintenance or simply the wrong environment. In other cases, certain types of acids or other substances can cause damage to stainless steel. Understanding the conditions and substances that can cause damage to stainless steel is essential for those looking to use it for a variety of applications.
Definition of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an incredibly durable material that has been used in a wide variety of applications for many years, ranging from decorative products to medical and industrial equipment. It is a metal alloy that contains at least 10.5% chromium, making it highly resistant to corrosion and rust. The chromium content also gives stainless steel its unique and attractive luster, making it a popular choice for many applications. But what can destroy stainless steel and its superior qualities? In this article, we’ll explore the various elements that can reduce the strength and durability of stainless steel and even cause it to corrode or rust. We’ll also discuss how to protect stainless steel from these damaging forces and keep it looking its best for years to come.
Chemical Corrosion
and Physical Damage
Stainless steel is a popular material known for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. It is often used in high-stress environments, such as food and beverage production, medical equipment, and transportation. However, stainless steel is not indestructible and can be damaged due to chemical corrosion and physical damage.
Chemical corrosion, also known as rust, is the most common way stainless steel deteriorates. This occurs when the metal is exposed to harsh acidic or alkaline chemicals, which cause the surface of the metal to corrode and weaken. The corrosion rate depends on the concentration, temperature, and duration of exposure to the chemical.
Physical damage is another way that stainless steel can be destroyed. This damage can be caused by environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, and abrasion. It can also be caused by mechanical impacts, such as bending, hitting, and scratching. These impacts can weaken the metal and make it more susceptible to corrosion.
The best way to protect stainless steel from chemical corrosion and physical damage is to ensure that it is properly maintained. This includes regularly inspecting the material for signs of damage and corrosion, as well as using protective coatings to prevent further damage. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your stainless steel will remain in good condition for years to come.
Mechanical Damage
Stainless steel is a durable material that is highly resistant to corrosion and erosion, making it an ideal material for a variety of applications. However, it is not invincible. Mechanical damage can weaken stainless steel and cause it to fail. Mechanical damage is any type of physical force that can cause wear, tear, or deformity. Examples include dropping, bending, scratching, denting, or hammering. Any of these can cause the steel to become brittle, or even crack. It can also cause the surface to become scratched or pitted, which can lead to further corrosion and erosion over time. To prevent mechanical damage, it is important to handle stainless steel with care, and to use the appropriate tools when manipulating it. It is also important to inspect the material regularly for any signs of wear or damage. With proper care, stainless steel can last for years without any major issues.
High Temperatures
and Corrosive Environments
Stainless steel is renowned for its impressive strength and durability, however, many people don’t realize that it can be vulnerable to damage. Two of the main causes of destruction to stainless steel are high temperatures and corrosive environments. High temperatures can weaken the material, leading to warping and corrosion. In addition, if exposed to extremely high temperatures, stainless steel can become brittle and crack. Furthermore, corrosion can occur in certain environments. This is caused by the presence of water, oxygen, and acidic compounds. The risk of corrosion increases when the environment is also exposed to high temperatures, salt, and other chemicals. To prevent this type of damage from occurring, it is important to use the correct grade of stainless steel for any given application and to protect the material from environmental stressors. Proper care and maintenance are essential to ensure that stainless steel maintains its strength and durability.
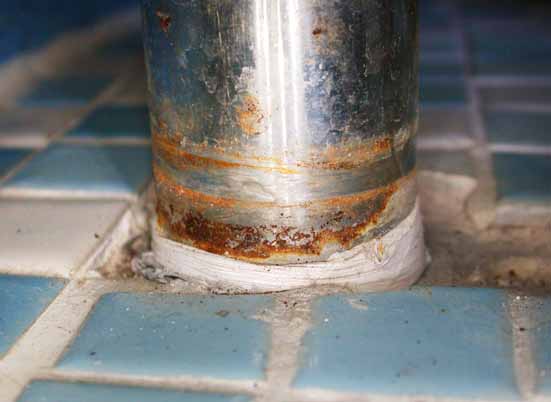

Stress Corrosion
Cracking
Stress Corrosion Cracking is one of the most common causes of destruction to stainless steel, and it can occur without warning. It is an electrochemical process that causes cracking and flaking of the metal in areas of high stress, and it is caused by a combination of corrosion, tensile stress, and a corrosive environment. This form of corrosion can be especially destructive in areas of high temperature, humidity, and salt deposits. The effects of Stress Corrosion Cracking can be difficult to detect until the damage is extensive, so it is important to check for signs of corrosion regularly. The best way to avoid Stress Corrosion Cracking is to properly maintain the stainless steel, and to use protective coatings to help reduce the risk of corrosion. If you are using stainless steel in a corrosive environment, it is essential to take the necessary precautions to ensure the metal does not become damaged.
Galvanic Corrosion
Stainless steel is renowned for its durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. But despite its impressive properties, it can still be susceptible to damage from certain environmental elements. One of the biggest threats to stainless steel is galvanic corrosion.
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals come into contact and an electrolyte is present. When the metals are placed in contact with the electrolyte, they create a galvanic cell, which causes the more active metal to corrode and deteriorate faster than the less active metal. This corrosion, which is also known as bimetallic corrosion, can be extremely damaging to stainless steel parts.
The most common causes of galvanic corrosion are the presence of marine environments, industrial chemicals, and salt fog. Marine environments contain a high concentration of electrolytes and can cause corrosion if two metals are in contact with each other. Industrial chemicals can also lead to corrosion when they come into contact with metal surfaces, and salt fog is another corrosive element that can damage stainless steel.
To prevent galvanic corrosion, it is essential to use the appropriate protective coatings on stainless steel surfaces. Protective coatings can help to minimize the effects of corrosion by providing a barrier between the two metals and the electrolyte. Additionally, it is important to choose the correct type of stainless steel for the application, as some grades are more resistant to corrosion than others. Finally, it is important to maintain the stainless steel surfaces regularly to ensure that any corrosive elements are removed before they cause any damage.
Contamination
is a major risk to stainless steel, as even the slightest impurities can corrode the material. This is due to the fact that stainless steel is an alloy of iron, chromium, and nickel, and any other metal or non-metal compounds can act as a catalyst for corrosion. Excessive exposure to water, salt, chemicals, and other contaminants can cause pitting, crevices, and other corrosion. Additionally, regular contact with acidic and alkaline substances can cause oxidation and discoloration. With that said, stainless steel is still highly resistant to corrosion, and proper maintenance can help keep the material in good condition and prevent it from being destroyed.
Prevention & Maintenance
.
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and durability, but it is still vulnerable to certain elements that can cause it to corrode, rust, or discolor. To ensure that your stainless steel products remain in pristine condition, it is essential to take preventative measures and practice regular maintenance.
To prevent corrosion, it is important to avoid exposing stainless steel to any of the elements that can damage it, such as chlorine, sulfur, and ozone. If you regularly use chemical cleaners, make sure to rinse the area thoroughly with water afterwards to prevent any residue from building up. Additionally, avoid storing metals of different compositions together, as this can cause galvanic corrosion.
Regular maintenance is also important for keeping stainless steel in good condition. To remove any dirt or residue, use a soft, non-abrasive cloth and warm, soapy water. After cleaning, rinse the stainless steel and dry it thoroughly, then apply a protective coating to prevent corrosion. Finally, inspect the stainless steel regularly for any signs of damage or discoloration.
By taking preventative measures and practicing regular maintenance, you can ensure that your stainless steel products stay in pristine condition and remain safe from any corrosive elements.
FAQs About the What Can Destroy Stainless Steel?
Q: What can corrode stainless steel?
A: Stainless steel can be corroded by certain chemicals, such as strong acids, chlorides, and sulfides. It can also be corroded by extreme temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, and oxygen.
Q: Can rust destroy stainless steel?
A: Rust can cause damage to stainless steel, but it is not the only cause of damage. Stainless steel can be damaged by a variety of substances and conditions, including strong acids, chlorides, sulfides, extreme temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, and oxygen.
Q: How can I protect stainless steel from corrosion?
A: To protect stainless steel from corrosion, you should avoid exposing it to strong acids, chlorides, and sulfides. Additionally, you should use proper cleaning and maintenance techniques, such as using only mild soap and water and avoiding strong detergents. You can also apply a protective coating to the steel to help protect it from corrosion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stainless steel is an incredibly durable material that is resistant to corrosion, rust, and most acids and bases. However, it is not completely indestructible. In certain circumstances, stainless steel can be damaged or destroyed by high temperatures, abrasion, and certain chemicals such as chlorides. It is important to be aware of these potential risks when handling stainless steel to ensure its longevity.